Decoding Data Spaces (part III): Organizations involved and main technologies
This article is the last in the series on Data Spaces. We will leave the previous articles here as a reference in case you missed them:
- In the first article we explore the fundamental pillars, roles, benefits, and challenges that these environments present for companies, thus serving as an introductory guide.
- In the second one, we analyze the technological aspects and key components that distinguish them from other technologies.
On this third installment, we will focus on the organizations involved, examining the role of entities such as DSBA, GAIA-X, IDSA, and DSSC, as well as presenting the different connectors that exist and the constant evolution of these ecosystems. We will also analyze the prominent role of Telefónica in this context.
Key organizations to consider
There are different organizations whose objective is to drive business transformation in the data economy. The Data Space Business Alliance (DSBA) was created with this goal in mind. This alliance is an initiative that unites the main players in the data industry to shape the future of this technology.
The members of the Data Spaces Business Alliance are, among others: Gaia-X, the Big Data Value Association (BDVA), the FIWARE, Foundation, and the International Data Space Association (IDSA). Let's take a look at what each of them does:
- GAIA-X: European initiative for the creation of an open, federated and interoperable data infrastructure. The stated goal of this GAIA is to ensure that Europe's companies and business models can be competitive and share data in a trusted environment.
- BDVA: Industry-driven research and innovation organization whose mission is to develop an innovation ecosystem that enables the digital transformation of the economy and society in Europe based on data and artificial intelligence.
- FIWARE: Non-profit organization that drives the definition and fosters the adoption of open standards (implemented through open-source technologies) that facilitate the development of smart solutions in domains such as smart cities, smart energy, agri-food and smart industry. Established in 2016, the foundation counts among its Platinum members Atos, Engineering, NEC, Red Hat, Telefónica, and Trigyn Technologies.
- IDSA: A non-profit organization dedicated to creating standards for data spaces. These standards are designed to ensure the secure exchange of data between participants within a specific governance framework, fostering trust and maintaining data sovereignty.
Together they represent many key industry players, associations, research organizations, innovators, and policy makers worldwide.
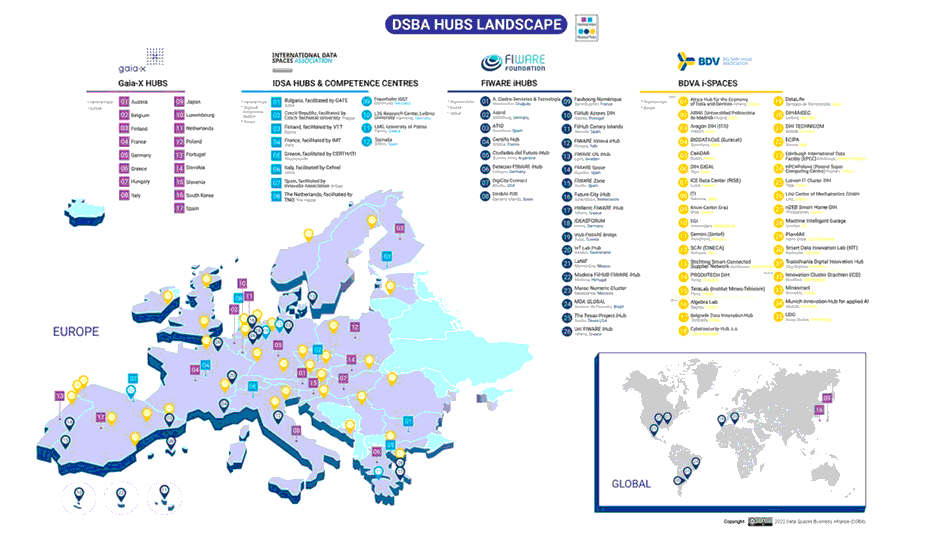 Figure 4. DSBA HUBspace
Figure 4. DSBA HUBspace
One more organization is also worth mentioning: the Data Spaces Support Centre (DSSC). DSSC aims to accelerate the formation of sovereign European data spaces, while maintaining control of the companies and individuals that generate the data and respecting EU values.
DSSC is funded by the European Commission as part of the Digital Europe Program and aimed at both the public sector and companies interested in creating sovereign data spaces. Its objective is to explore the needs, common requirements and best practices of existing data space initiatives, as well as to provide guidelines and support to accelerate the creation of new data spaces that enable data sharing while respecting the principles of data sovereignty, interoperability and trust.
Apart from organizations, there is also a wide landscape of options at the technology level. Let's see what connectors are on the market.
Connectors
This component is basic to participate in any ecosystem that takes the form of a Data Space. Its main functions are to provide a point-to-point connection between two entities: the data provider (which sends the data) and the data consumer (which receives the data). It contains the entity's identifier and allows managing its participation in the ecosystem. It manages the transfer of data between the data provider and the data consumer, registering this transfer in the Clearing House. It allows the data provider to publish the metadata describing the information available, the terms of use and billing.
This component is key to enabling secure and reliable participation in the data exchange ecosystem, managing the connection, metadata and data transfer between providers and consumers. The main features of the connector are:
- Trust: Trust is the basis of data spaces. This is achieved through evaluation and certification prior to access granted to the data space.
· Data security and sovereignty: Secure data exchange, thus maintaining control over data through security protocols and policy implementation.
Data decentralization: Decentralization is a crucial aspect of data spaces, with the principle of keeping data as close as possible to its origin and sharing it only when explicitly allowed.
Interoperability: Standardized communication patterns between connectors enable the creation and interoperability of different connector implementations.
There are multiple connectors, with varying degrees of development, maturity, and objectives. The following is a summary table updated to 2024.
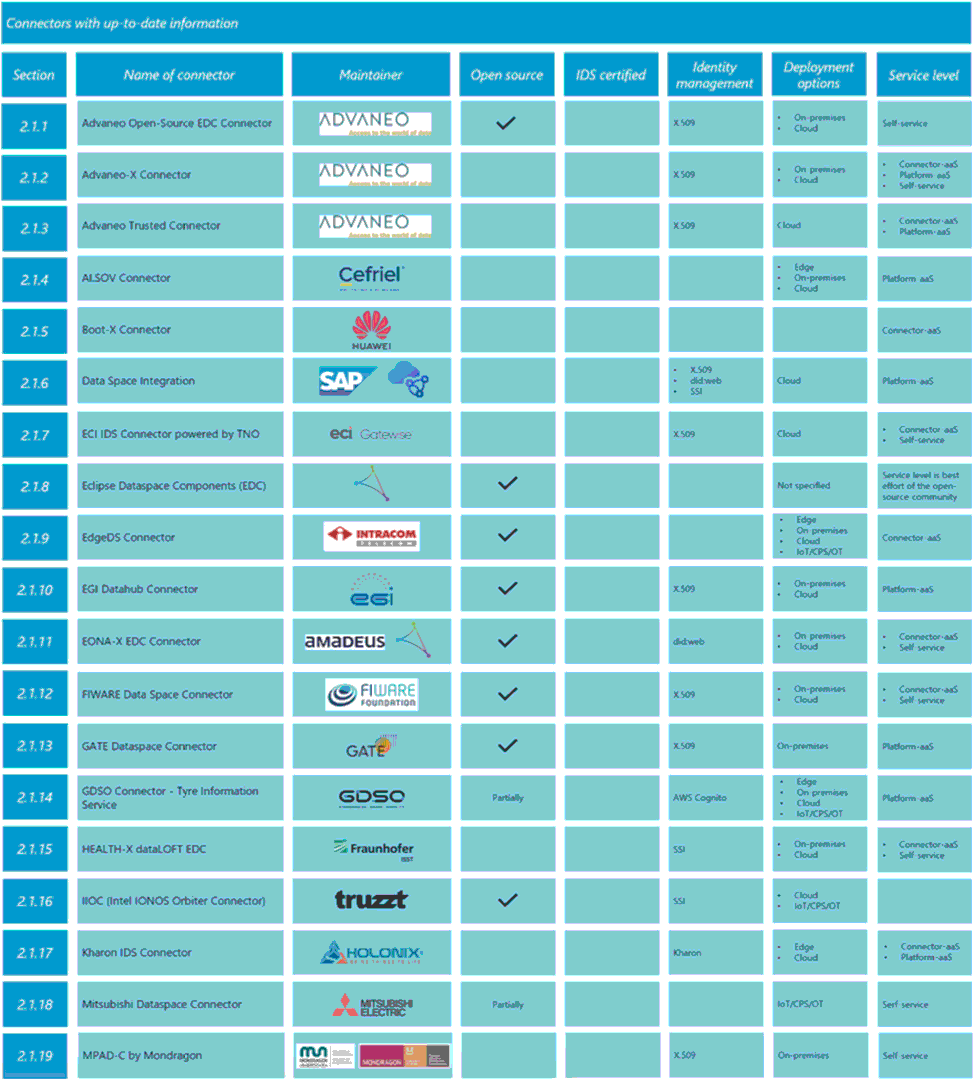 Image source: Data Connector Report May 2024. International Data Spaces Association
Image source: Data Connector Report May 2024. International Data Spaces Association
As relevant connectors, we can highlight Eclipse Data Components, which is becoming a de facto standard for many ecosystems. Another consolidated project in the industry would be FIWARE, which started with a focus on Smart Cities, but has extended its field of action.
Telefónica in Data Spaces
We have played an important role at Telefónica in the promotion and development of Data Spaces. As a member of the Gaia-X Spain Association and a member of the board of directors of GAIA-X Spain, Telefónica has been committed to the promotion of Data Spaces. The company has organized events for GAIA-X Spain, where data spaces and the European GAIA-X initiative were addressed, with the aim of promoting the data economy and fostering networking among participants.
The company has also been an active part of the FIWARE initiative, an open source platform that promotes the creation of standards for the development of Smart applications in different areas, such as Smart Cities, Smart Ports, Smart Logistics, and Smart Factories.
In collaboration with other organizations such as Atos, Engineering and Orange, at Telefónica we have contributed to the development of FIWARE standards, which led to the creation of the FIWARE Foundation in 2016. This foundation supports FIWARE activities, protecting the brand and promoting the principles of openness, transparency, and meritocracy in the community.
Telefónica has been a key player in the consolidation of FIWARE as a reference platform for the development of solutions and applications in sectors such as IoT. The company has worked to make FIWARE a neutral and open standard, without being tied to any specific vendor. The FIWARE Foundation continues to grow and expand its open-source ecosystem with more than 2,000 members, with the addition of relevant members such as Amazon Web Services and Red Hat.
A future in constant evolution
The creation and development of Data Spaces in Spain is constantly evolving, thanks to the collaboration between companies, institutions and organizations. Telefónica's initiative in this area is an example of how the industry can work together to create an open and secure data ecosystem.
Data Spaces have the potential to transform the way businesses and organizations work with data, and to create new opportunities for innovation and growth. However, it also poses challenges and challenges that must be effectively addressed.
In this sense, Telefónica's experience and commitment to creating Data Spaces can be a model for other companies and organizations to follow. Its work in the GAIA-X initiative and its support for the creation of standards through FIWARE are examples of how collaboration and innovation can lead to an improved technology marketplace.
AUTHORS
Santiago Morante
AI Alliances and Solutions Development Manager
Paula Valles
Data Sales Consulting
* * *
Imagen: rawpixel.com / Freepik.
 Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud Cyber Security & NaaS
Cyber Security & NaaS AI & Data
AI & Data IoT & Connectivity
IoT & Connectivity Business Applications
Business Applications Intelligent Workplace
Intelligent Workplace Consulting & Professional Services
Consulting & Professional Services Small Medium Enterprise
Small Medium Enterprise Health and Social Care
Health and Social Care Industry
Industry Retail
Retail Tourism and Leisure
Tourism and Leisure Transport & Logistics
Transport & Logistics Energy & Utilities
Energy & Utilities Banking and Finance
Banking and Finance Smart Cities
Smart Cities Public Sector
Public Sector

.jpg)