Cyber Security professionals in demand
The shortage of skilled talent is part of the 'perfect storm' forming within the Cyber Security sector: a global deficit of specialized professionals amounts to approximately 40%.
Meanwhile, cyber threats become increasingly complex and perilous. State actors and cybercriminals employ advanced tactics to conduct espionage, influence operations, and disrupt critical infrastructure. Meanwhile, cyberattacks continue to rise, including ransomware attacks, supply chain breaches, and persistent advanced threats.
This combination endangers the daily operations of businesses, threatens resilience and continuity, and jeopardizes critical infrastructure.
Last year cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructures such as energy and transportation increased by 35%.
Against this backdrop, companies face a dual challenge: the urgent need to protect themselves against advanced threats and the difficulty of recruiting and retaining qualified talent.
Cyber Security shortage talent problem
Factors contributing to this talent shortage include the accelerating number of cyber threats and the constant evolution of attack techniques employed by adversaries.
Additionally, the pace at which technology advances surpasses the capacity of educational programs to prepare adequately trained and certified cybersecurity professionals.
Demand for experts has intensified, boosting labor market competitiveness as companies strive to attract and retain top talent.
Consequences of talent shortage
The lack of specialized cybersecurity personnel exacerbates risks posed by cyber threats, compelling companies to adopt more innovative approaches to recruitment and retention strategies. Additionally, implementing advanced technological solutions rooted in automation and artificial intelligence (AI) is essential to enhance cybersecurity teams' efficiency and effectiveness.
An insufficient cybersecurity workforce can have severe consequences for businesses, including:
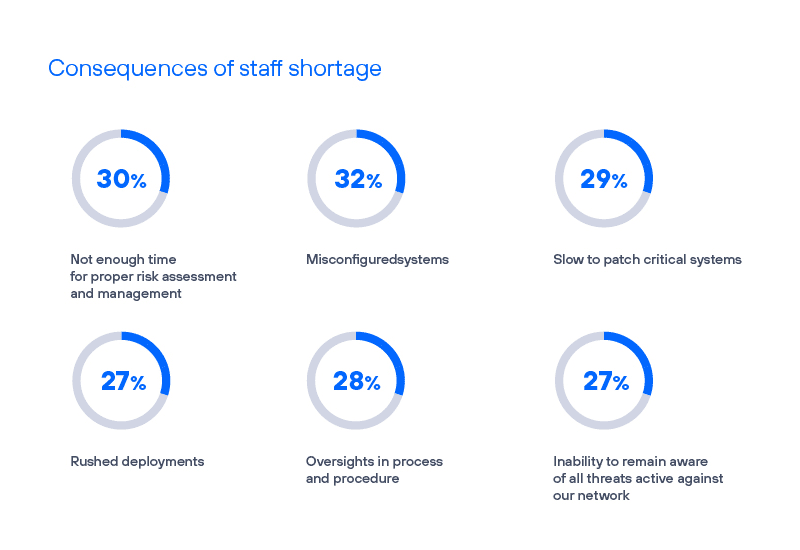 Prevalence of specific problems caused by personnel shortage.
Prevalence of specific problems caused by personnel shortage.
- Inadequate risk management: Without sufficient risk analysts, companies may fail to identify or mitigate risks promptly.
- Poorly configured systems: A lack of skilled personnel can lead to system misconfigurations, leaving vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Delayed patching: Inadequate patch application leaves businesses exposed for prolonged periods.
- Delays in deployment: Without sufficient resources, companies may struggle to deploy protective solutions quickly, compromising security from the start.
- Human error in procedures: A lack of skilled personnel can result in procedural errors in implementing safety policies and practices.
- Inability to stay informed on active threats: The vast array of cyber threats and their rapid evolution can cause companies to miss critical threats, increasing the risk of security breaches.
Cyberresilience is crucial for businesses facing complex cybersecurity challenges. It combines talent, holistic strategies, and advanced technologies.
Specialized Cyber Security profiles
Recognizing the growing complexity of cyber threats, we have identified the most demanded specialized profiles in Cyber Security to address and respond effectively to security incidents. Among them are:
- Incident Response Expert: Manages and coordinates the response to security incidents, ensuring threats are contained, investigated, and mitigated efficiently.
- Threat Hunter: Actively searches for cyber threats within an organization's infrastructure using advanced techniques to detect and neutralize malicious actors before they cause significant damage.
- Intelligence Threat Analyst: Collects, analyzes, and notifies information on cyber threats to anticipate and prevent potential attacks, providing strategic insights to enhance organizational security posture.
- Digital Forensics Analyst: Conducts thorough digital evidence analysis to investigate incidents, identifying the root cause of attacks and aiding in incident recovery and fortification efforts.
- Malware Expert: Studies and analyzes malicious programs to understand their functionality, developing countermeasures and protecting organization systems from infections and cyberattacks.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is a strategic and business priority requiring collaboration among multiple specialized experts. Cyberresilience not only safeguards an organization's assets but also ensures customer confidence and business sustainability in increasingly complex environments.
Implementing robust policies, continuously training the workforce, and adapting to new technologies and regulations are essential for maintaining an effective and proactive security posture.
While budget constraints may limit a company's ability to manage cybersecurity measures, efficient implementation of protective strategies is crucial to preserve defense quality, maintain business continuity, and ensure cyberresilience.
 Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud Cyber Security & NaaS
Cyber Security & NaaS AI & Data
AI & Data IoT & Connectivity
IoT & Connectivity Business Applications
Business Applications Intelligent Workplace
Intelligent Workplace Consulting & Professional Services
Consulting & Professional Services Small Medium Enterprise
Small Medium Enterprise Health and Social Care
Health and Social Care Industry
Industry Retail
Retail Tourism and Leisure
Tourism and Leisure Transport & Logistics
Transport & Logistics Energy & Utilities
Energy & Utilities Banking and Finance
Banking and Finance Smart Cities
Smart Cities Public Sector
Public Sector





