Cybersecurity, security and safety: key differences between and how to apply them in AI, IoT and other next-gen technologies
We explore the differences and relationships between the concepts of 'safety', 'security' and 'cybersecurity' in the context of disruptive technologies such as AI, autonomous vehicles and quantum infrastructures. We highlight the importance of a holistic approach to managing accidental, intentional and digital risks, ensuring the protection of people, systems and digital ecosystems.
______
Imagine an autonomous vehicle that brakes sharply to avoid hitting a pedestrian: safety ensures the protection of human lives. When that same vehicle withstands an unauthorized remote access attempt by a malicious actor, security ensures the integrity of the system. And when the data powering its navigation is protected from manipulation or theft, cybersecurity ensures trust in the digital ecosystem.
■ As autonomous systems, AI and quantum infrastructures reshape sociotechnical landscapes, the ability to distinguish — and at the same time integrate — safety, security and cybersecurity becomes a methodological imperative and a prerequisite for resilience, legitimacy and sustainable innovation.
In today’s world of next-gen, emerging and disruptive technologies, from AI to quantum computing and industrial IoT, these three terms (safety, security and cybersecurity) are often used interchangeably — but they serve distinct and complementary purposes.
Misunderstanding their differences is more than just a semantic issue; it can lead to weak governance, fragmented risk management, and vulnerabilities that propagate system-wide.
That’s why we explore how safety, security and cybersecurity intersect in practice — where boundaries matter — and how organisations can address them holistically to protect not only systems, but also people, economies and digital trust.
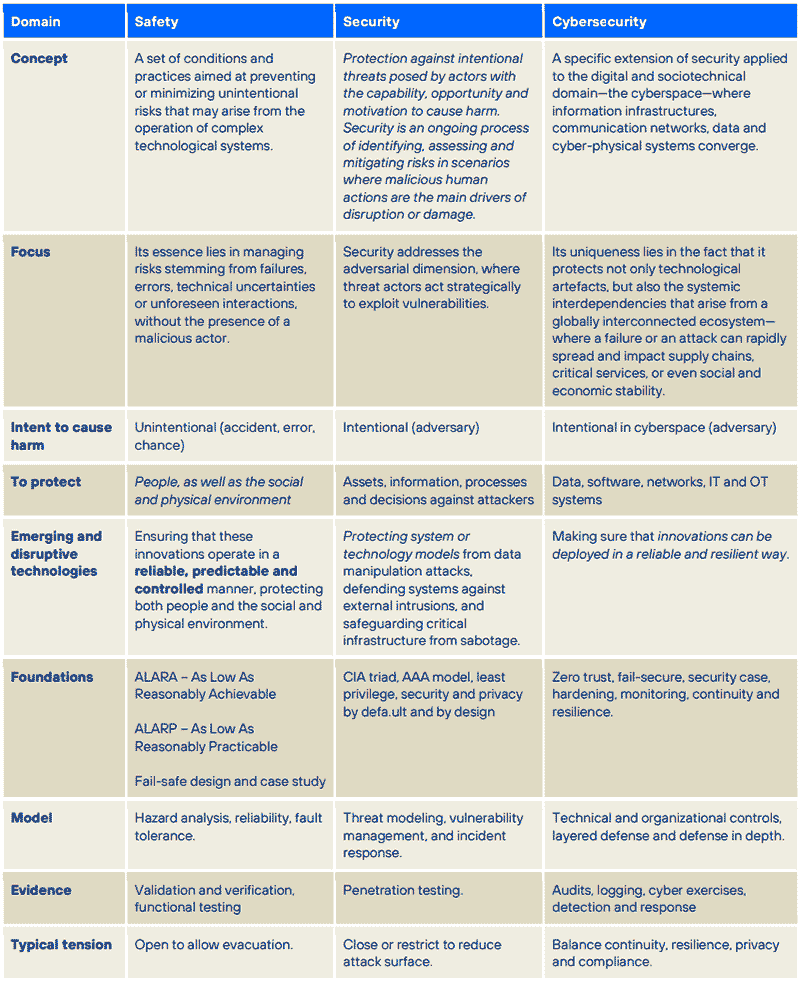
■ The tension between the accidental, the intentional, and the systemic-digital reveals that controlling advanced technologies requires not only technical controls and capabilities, but also a holistic approach able to address uncertainty, antagonism and interconnectivity as interwoven sources of risk.
As a practical case, we’ll look at AI Safety, AI Security, and AI Cybersecurity
AI Safety (In the context of care and alignment)
Preventing unintentional harm caused by the behaviour of AI systems, such as: poorly defined goals and requirements, specification gaming, spurious generalisation, hallucinations, bias, loss of control, and systemic externalities (disinformation, job displacement, social risks). This includes alignment with interpretability, deployment governance, and sociotechnical use cases.
AI Security (In the context of protection against malicious actors)
Protecting AI systems from attacks: data poisoning, model theft/inversion, prompt injection/jailbreaks, backdoors, manipulation of the supply chain (datasets, parameters, libraries). This relies on machine learning (ML)-specific threat modeling, testing by security teams, and controls across the secure machine learning operations lifecycle (MLOps).
AI Cybersecurity (In the context of application and use)
- Cybersecurity of AI: Protecting the digital ecosystem that supports AI (data, models, APIs, cloud/edge or hybrid infrastructure). In practical terms, this often overlaps with AI Security, but with a stronger focus on cyber controls.
- AI Cybersecurity: Using AI to enhance offensive or defensive cybersecurity capabilities, such as event detection, anomaly identification, malware classification, next-generation SOAR, and more. It’s essential to clarify which of the two definitions we are applying.
From an epistemological perspective, safety, security and cybersecurity represent interrelated but distinct dimensions of protection that, together, define the reliability of emerging and disruptive technologies. Here's the key:
- Safety: Addresses unintentional risks inherent to complex systems, ensuring reliability and minimising accidental harm.
- Security: Focuses on intentional threats, particularly hostile or malicious actions and exploitation.
- Cybersecurity: Extends security to the digital and sociotechnical domain, safeguarding interconnected infrastructures and assets in cyberspace.
Together, these concepts form a triad where tensions and synergies coexist: for example, a design that maximises safety by allowing systems to fail openly may conflict with security principles that require strict containment.
■ In the era of next-gen technologies, the line between accidents, adversarial actions and digital threats collapses into a single continuum of vulnerability, where safety, security and cybersecurity are no longer separate domains, but rather interdependent conditions of technological trust.
Therefore, in the governance of technologies like AI, autonomous vehicles or quantum infrastructures, an integrated approach is essential — one that not only differentiates between accidental and adversarial risks, but also acknowledges the systemic interdependencies between technical, organisational and geopolitical layers.
Ultimately, this highlights the need for holistic frameworks that align safety assurance, security engineering practices, and cyber resilience to ensure technological innovation remains both beneficial and sustainable.
 Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud Cyber Security & NaaS
Cyber Security & NaaS AI & Data
AI & Data IoT & Connectivity
IoT & Connectivity Business Applications
Business Applications Intelligent Workplace
Intelligent Workplace Consulting & Professional Services
Consulting & Professional Services Small Medium Enterprise
Small Medium Enterprise Health and Social Care
Health and Social Care Industry
Industry Retail
Retail Tourism and Leisure
Tourism and Leisure Transport & Logistics
Transport & Logistics Energy & Utilities
Energy & Utilities Banking and Finance
Banking and Finance Smart Cities
Smart Cities Public Sector
Public Sector





