Getting started with Google AI Studio: from idea to functional web app in minutes
Turning an idea into a functional web application has traditionally required learning programming languages and environments, even for simple goals. As a result, many ideas never went beyond sketches or intentions.
This barrier explains the growing interest in approaches like AI-assisted development, which lowers the entry threshold.
Vibe coding and Google AI Studio for building and prototyping web apps with AI
Vibe coding is one of these AI-assisted approaches. It enables users to start building applications without yet mastering the technical ecosystem, even just to experiment or create prototypes. It also allows for the inclusion of technologies or programming languages beyond one’s current skillset.
This technique lets you build websites or apps by clearly describing what you want to create and how it should behave. However, as projects scale, technical understanding, including coding, becomes critical for creating secure, efficient, and scalable systems.
Within this context, Google AI Studio is an accessible and even fun entry point for experimenting and prototyping. It’s a web-based platform with a very low usage cost, even zero at initial tiers. It’s designed for testing ideas, rapid iteration, and concept validation, even without prior experience. When needed, the generated code can be transferred to more advanced workflows.
Google AI Studio allows you to turn ideas into functional prototypes and validate concepts, even without programming skills.
Getting started with Google AI Studio
To access Google AI Studio, simply log in with your Google account. The interface is simple and intuitive, and you can start using the service right away. However, it's helpful to review two settings in the right-hand configuration panel:
- Model: Gemini 3 Flash Preview is the default option, and thanks to its low latency, it’s a great starting point for try and learn sessions.
- System Instructions: as with most AI models, you can define a role or directive for the assistant. While optional, this helps guide the AI with a specific prompt such as:
Act as an expert Full Stack developer. Create modern, responsive, and functional web apps using HTML and CSS for layout and pure JavaScript. Focus on clean visual design without using color gradients.
Describing the project
The main chat area is where you describe the app idea, what it should do and how it should work. It’s not about asking for “something that works,” but rather defining the problem, usage context, and the app or website’s core logic.
Instead of simply asking for an “inventory management website,” provide details on the app’s purpose, functionality, and visual design.
You can write the prompt directly, or after discussing your idea with Gemini as if you were talking to a teammate. For example:
> I want to build an inventory management app for a small store. It should include a form to add products, a real-time search bar, color-coded tags based on stock levels, and the ability to save data locally in the browser so it persists between uses.
Once the code is generated, the next step is to review and test the app: does the interface behave as expected, do the data persist, is the interaction flow clear, and does the logic match the original intent?
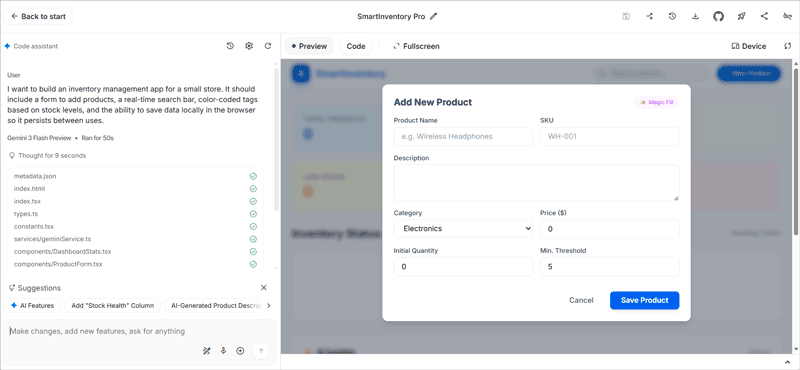 Example of a web app generated by Gemini in Google AI Studio.
Example of a web app generated by Gemini in Google AI Studio.
If something doesn’t work, you don’t need to fix the code manually. Just describe the issue (copy any error messages, if present) and ask the model for a specific fix.
—For example, “The search bar doesn’t filter when the field is empty”, “Add a visual confirmation after saving”, or “Separate the form from the list to improve readability”.
This ongoing dialogue with Gemini (initial prompt, generation, testing, observation, correction) shortens the gap between idea and outcome. Even without understanding every line of code, you’re still defining what should happen, when, how, and what it should look like.
Local testing: from AI to browser
Once Gemini provides the response, the interface displays the app code in a structured format that you can download and run locally on your computer:
- The Code tab shows a list of generated files (e.g.,
index.html, script.js, styles.css). - Each file includes a download icon to save it locally.
- All downloaded files must be saved in the same folder.
- Double-clicking
index.htmlwill open the app in your browser, running independently, outside of AI Studio. - You can also download the complete app as a .zip file using the Download app option.
Sharing and publishing your app online
Google AI Studio provides direct integration with GitHub, so your app can be accessed from anywhere. Clicking Save to GitHub and authorizing access will create a repository with the final generated code.
—Syncing with GitHub provides a backup, version history, and a launchpad for sharing or publishing your app.
To publish or share your app online, you can use GitHub Pages (enabled via the repository settings). This makes your app available via a public URL like https://username.github.io/project/. You can also deploy it using traditional hosting or platforms like Netlify.
—Similarly, the Deploy app button in Google Cloud lets you push your app to Google’s infrastructure (via Cloud Run).
⚠️ Security and API Keys: If your app needs to connect to the Gemini API for complex tasks (like generating images or analyzing data), make sure not to expose your API keys. Avoid sharing files that contain your API Key in the code, and remove any embedded credentials before publishing or sharing your app.
More: Critical API security rules for Gemini.
Conclusion
Google AI Studio doesn’t replace coding or professional development environments (even AI-assisted ones), but it offers a clear and accessible starting point to explore the potential of AI in app creation.
Above all, it’s an invitation to experiment, explore, and get started in a gradual and accessible way, helping ideas quickly become functional prototypes.
In this context, it’s crucial to know how to frame a problem, define behaviors, and evaluate results. While technical knowledge is still important, especially as projects scale, anyone looking to explore, shape an idea, test a concept, or start building apps now has an accessible on-ramp to take action.
 Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud Cyber Security & NaaS
Cyber Security & NaaS AI & Data
AI & Data IoT & Connectivity
IoT & Connectivity Business Applications
Business Applications Intelligent Workplace
Intelligent Workplace Consulting & Professional Services
Consulting & Professional Services Small Medium Enterprise
Small Medium Enterprise Health and Social Care
Health and Social Care Industry
Industry Retail
Retail Tourism and Leisure
Tourism and Leisure Transport & Logistics
Transport & Logistics Energy & Utilities
Energy & Utilities Banking and Finance
Banking and Finance Smart Cities
Smart Cities Public Sector
Public Sector